Contribution Margin Ratio Formula, Calculation, and Example
The contribution margin ratio represents a company’s revenue minus variable costs, divided by its revenue. In short, it is the proportion of revenue left over after paying for variable costs. As mentioned earlier, the contribution margin ratio can help businesses determine the lowest possible price at which sales can be made and still break even. This analysis can aid in setting prices, planning sales or discounts, and managing additional costs like delivery fees.
Resources
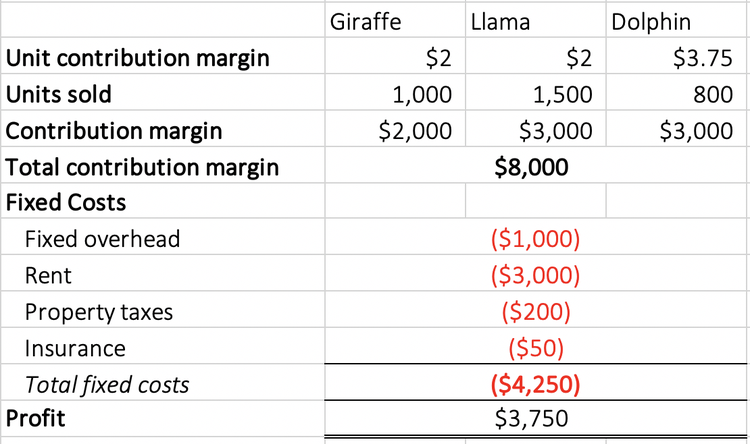
Suppose you’re tasked with calculating the contribution margin ratio of a company’s product. For this section of the exercise, the key takeaway is that the CM requires matching the revenue from the sale of a specific product line, along with coinciding variable costs for that particular product. However, the contribution margin facilitates product-level margin analysis on a per-unit basis, contrary to analyzing profitability on a consolidated basis in which all products are grouped together.

Business Class
Accordingly, the per-unit cost of manufacturing a single packet of bread consisting of 10 pieces each would be as follows. One packet of whole wheat bread requires $2 worth of raw material. The electricity expenses of using ovens for baking a packet of bread turns out to be $1. My Accounting Course is a world-class educational resource developed by experts to simplify accounting, finance, & investment analysis topics, so students and professionals can learn and propel their careers.
Step 2 of 3
- If they sold \(250\) shirts, again assuming an individual variable cost per shirt of \(\$10\), then the total variable costs would \(\$2,500 (250 × \$10)\).
- That is, it refers to the additional money that your business generates after deducting the variable costs of manufacturing your products.
- A business can increase its Contribution Margin Ratio by reducing the cost of goods sold, increasing the selling price of products, or finding ways to reduce fixed costs.
- For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing.
- The contribution margin can be stated on a gross or per-unit basis.
Analyzing the contribution margin helps managers make several types of decisions, from whether to add or subtract a product line to how to price a product or service to how to structure sales commissions. Before making any major business decision, you should look at other profit measures as well. The contribution margin ratio is the percentage of sales revenues, service revenues, or selling price remaining after subtracting all of the variable costs and variable expenses. The contribution margin ratio is just one of many important financial metrics used for making better informed business decisions.
Contribution Margin vs. Gross Margin: What is the Difference?
This cost of the machine represents a fixed cost (and not a variable cost) as its charges do not increase based on the units produced. Such fixed costs are not considered in the contribution margin calculations. The contribution margin is different from the gross profit margin, the difference between sales revenue and the cost of goods sold. While contribution margins only count the variable costs, the gross profit margin includes all of the costs that a company incurs in order to make sales.
Such an analysis would help you to undertake better decisions regarding where and how to sell your products. Conceptually, the contribution margin ratio reveals essential information about a manager’s ability to control costs. adjusted net income The contribution margin may also be expressed as a percentage of sales. When the contribution margin is expressed as a percentage of sales, it is called the contribution margin ratio or profit-volume ratio (P/V ratio).
11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. The best contribution margin is 100%, so the closer the contribution margin is to 100%, the better. The higher the number, the better a company is at covering its overhead costs with money on hand. Aside from the uses listed above, the contribution margin’s importance also lies in the fact that it is one of the building blocks of break-even analysis. With that all being said, it is quite obvious why it is worth learning the contribution margin formula.
As of Year 0, the first year of our projections, our hypothetical company has the following financials. As the first step, we’ll begin by listing out the model assumptions for our simple exercise. We’ll now move on to a modeling exercise, which you can access by filling out the form below.
The ratio can help businesses choose a pricing strategy that makes sure sales cover variable costs, with enough left over to contribute to both fixed expenses and profits. It can also be an invaluable tool for deciding which products may have the highest profitability, particularly when those products use equivalent resources. In general, the higher the contribution margin ratio, the better, with negative numbers indicating a loss on every unit produced. Contribution margin analysis also helps companies measure their operating leverage. Companies that sell products or services that generate higher profits with lower fixed and variable costs have very good operating leverage. As mentioned above, the contribution margin is nothing but the sales revenue minus total variable costs.
Thus, the level of production along with the contribution margin are essential factors in developing your business. Now, it is essential to divide the cost of manufacturing your products between fixed and variable costs. Variable costs are not typically reported on general purpose financial statements as a separate category. Thus, you will need to scan the income statement for variable costs and tally the list. Some companies do issue contribution margin income statements that split variable and fixed costs, but this isn’t common.


Commenti recenti